Project Management Guide
Project Management Guide
What Is Project Management?
What Is a Project?
Why Is Project Management Important?
Project Life Cycle Phases
- Project Initiation
- Project Planning
- Project Execution
- Project Monitoring
- Project Closure
Project Management Methodologies
- Waterfall Project Management
- Critical Path Method
- Critical Chain Project Management
- Agile Project Management
- Scrum Project Management
- Kanban Project Management
- Lean Project Management
- Six Sigma Project Management
- PRINCE2
- PRiSM
- PMBOK Method
Project Management FAQ
Six Sigma Project Management
The Six Sigma methodology was introduced by Motorola around three decades ago to compete with the lean manufacturing business model of Japan. The Six Sigma revolution that followed was fueled by countless keen executives and managers charmed by its ability to cut down on cycle time, get rid of product defects, and substantially increase customer satisfaction and involvement. Today, it is hotter than ever.
But can this methodology benefit you?
To answer that, you need to first expand your understanding of what Six Sigma methodology is and how it works. This handy guide outlines everything you need to know about Six Sigma, to evaluate whether you should adopt it or not.
What Is the Six Sigma Methodology?
The Greek alphabet Sigma (?) is used by statisticians to measure the variability in any process. In Sigma methodologies, the sigma level of a company’s business processes is used to measure its performance.
While three and four sigma performance levels were a norm at one point, they were soon replaced by Six Sigma when companies realized that it offers only 3.4 problems per million opportunities against 6,200 to 67,000 problems per million opportunities allowed by the other two. In fact, companies operating at three or four sigma typically spend 25% to 40% of their revenues fixing defects, whereas the ones operating at six sigma, less than 5%.
By employing a set of quality management methods, Six Sigma identifies and removes the causes of defects in a process. Unlike traditional cost-cutting plans, which directly affect the quality of the product or service too, Six Sigma pins down and eliminates “waste” costs — costs that offer no value to the customer.
How Does Six Sigma Project Management Help You?
While Six Sigma ensures that the defects of an operational process are removed to never return, project management aims at controlling potential problems on a project-to-project basis. Since Six Sigma is a project itself, using project management techniques can help in its smooth employment.
Here is how Six Sigma project management can help you:
1. Improved Efficiency
Six Sigma offers proper project planning with defined roles and a data-driven strategy. When you add the benefit of having more time on your teammates’ hands because of reduced defects, your organization as a whole will enjoy improved productivity.
2. Data-Driven Decision Making
Since the Six Sigma approach is entirely statistical, it can positively affect your decision-making process by allowing you to make an informed decision based on proper analysis.
3. Reduced Costs
The decrease in defects and the increase in operational efficiency automatically leads to reduced costs of operations.
4. Increased Collaboration
Six Sigma’s organization-inclusive approach allows different team members and departments to effectively collaborate with each other to identify problems and work on solutions.
Read More: Team Building Exercises for Better Collaboration in Project Teams
5. Improved Customer Satisfaction
Six Sigma’s focus on reducing the causes of variations from how the customer’s requirements were defined lead to a more refined output and satisfied customer.
How Can You Implement It?
Years of trial and error in terms of implementations by several companies have now allowed us to have documented steps to ensure you can successfully implement Six Sigma.
- Provide senior leadership with training in the principles and tools they need, to prepare the organization for success.
- Cultivate an environment for innovation and creativity in the organization.
- Develop systems to establish close communication with employees, customers, and suppliers.
- Develop a framework for continuous process improvement.
- Determine the indicators for monitoring and marking progress.
Popular Six Sigma Methodologies
Six Sigma takes a handful of proven methods and trains the ‘Black Belts’ to a high level of proficiency in their application. The tools and techniques are applied within a simple performance improvement model for both existing and not-yet-implemented processes.
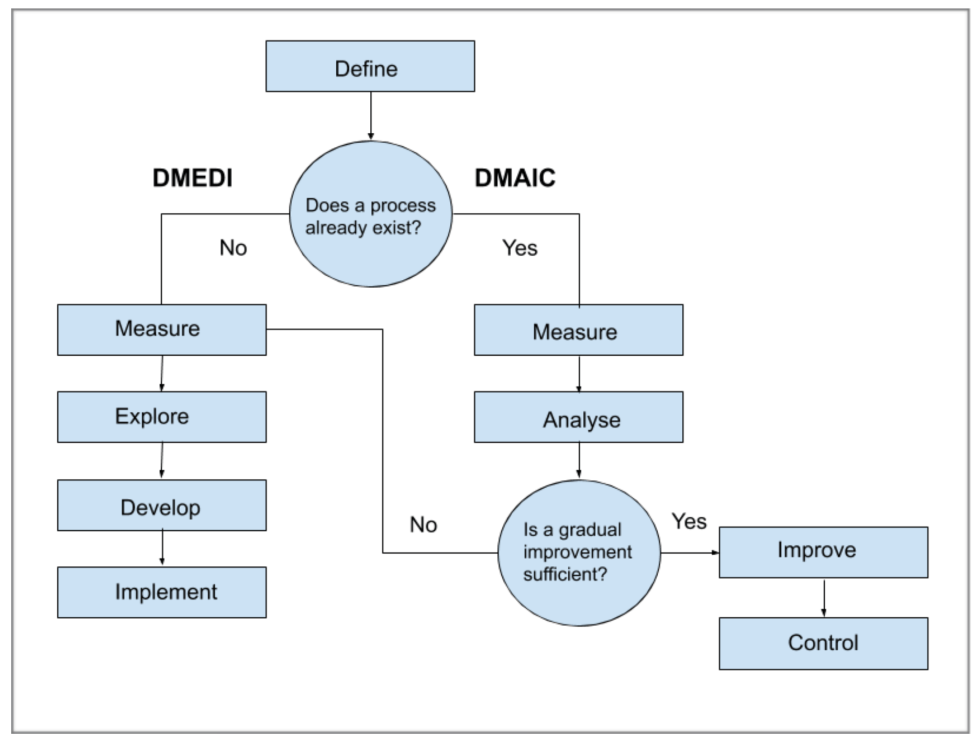
DMAIC: To Improve Existing Processes
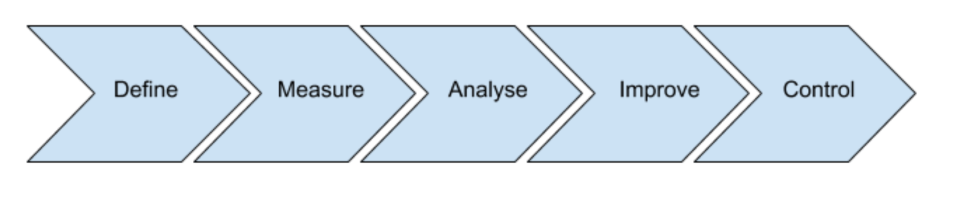
- Define: Identify the goals of the project and the customer requirement.
- Measure: Quantify the problem to determine the current performance.
- Analyze: Evaluate the data to find the root cause.
- Improvement: Eliminate the root cause identified in the last phase.
- Control: Sustain the improved process performance.
DMEDI: To Implement a New Process
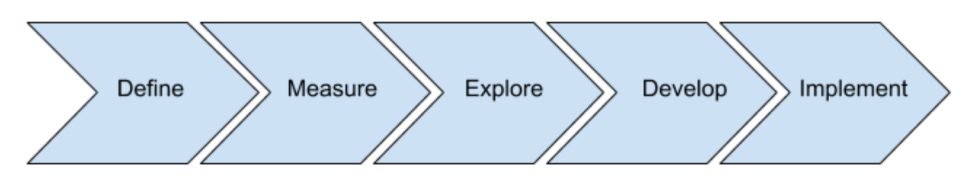
- Define: Identify the goals of the project and customer requirements.
- Measure: Quantify the problem to determine the current performance.
- Explore: Examine conceptual designs.
- Develop: Produce detailed process designs.
- Implement: Validate the design with a pilot-test.
What Are Six Sigma’s Shortcomings?
Like all methodologies, Six Sigma has to endure its fair share of criticism too. The Harvard Business Review lists some of them:
- Most companies are unable to implement the statistical approach they settle on.
- Six Sigma doesn’t incorporate information technology to improve processes.
- The methodology is elitist since it makes the Black Belt solely responsible for process improvement.It supports incremental improvements, not radical breakthroughs.
- It doesn’t assist innovation-oriented work.
- Of course, not all organizations have to necessarily struggle with Six Sigma. In many, the methodology plays an impressive role because of its ability to reduce defects to one in six standard deviations.
Are You Ready to Start Your Six Sigma Journey?
With complete information on what Six Sigma constitutes, how it can benefit you, and the flaws you may have to deal with, you can now make an informed decision regarding whether you wish to implement Six Sigma project management or not. If you do choose to apply it, ensure everyone in the organization, especially the top executives, are committed to making efforts towards turning it into a success.
