Project Management Guide
Project Management Guide
What Is Project Management?
What Is a Project?
Why Is Project Management Important?
Project Life Cycle Phases
- Project Initiation
- Project Planning
- Project Execution
- Project Monitoring
- Project Closure
Project Management Methodologies
- Waterfall Project Management
- Critical Path Method
- Critical Chain Project Management
- Agile Project Management
- Scrum Project Management
- Kanban Project Management
- Lean Project Management
- Six Sigma Project Management
- PRINCE2
- PRiSM
- PMBOK Method
Project Management FAQ
What Is Cost Management in Project Management?
According to a Project Management Institute report, only 57% of IT companies could complete their projects within their initial budget. This figure means that nearly 43% of organizations end up overspending and exceeding their budget targets. Naturally, it is a cause of concern for Project Managers as their projects are losing money or at least eroding their margins. They also leave an impact on future projects. So how can they address this issue and resolve it?
The answer is simple – through project cost management.
In this article, we will look at the concept of project budgeting, with a focus on cost management. We will also explore the elements of a cost management plan, along with its importance and drawbacks.
What is Project Cost Management?

For a project to be considered as “successful,” it needs to satisfy the following criteria:
- It should deliver on the project scope and requirements
- The project performance and execution quality should be of a high standard
- It should be complete within the stipulated project schedule
- It should be complete within budget
Project managers need to carry out cost control to fulfill the final criteria. And this is where project cost management enters the picture.
As the name indicates, project cost management involves the estimation, budget creation, allocation, and control over project costs throughout its entire lifecycle. It serves as a baseline against which the project cost performance is measured.
As such, the primary purpose of project cost management is to ensure that the spending remains within the approved budget.
Importance of Cost Management
The importance of cost management is glaringly obvious – to manage project costs. When you start working on a project, estimating costs is one of the first activities that you carry out. It offers you a sense of how much you should spend on the project, which you can then classify into the cost per sub-task.
After developing a project budget and allocating it, you can then make other decisions that have cost implications. For example, you can decide on the tools and technologies that you need to deploy for the project, the vendors for such products, the human resources necessary, the level of skill and expertise of the team members, etc.
Predetermining the budget mitigates cost overruns. Additionally, it can help:
- Define clear and achievable project goals to the stakeholders.
- Negotiate on the scope with the customers.
- Track progress in real-time and carry out corrective action in case of deviations.
- Avoid losing money on the project by maintaining margins.
- Develop data that can serve as a benchmark for future projects.
From the above, it becomes abundantly clear that project cost management forms the backbone of project management.
Pillars of a Cost Management Plan
While project cost management is a highly dynamic and continuously evolving entity, a standard cost management plan contains the following elements:
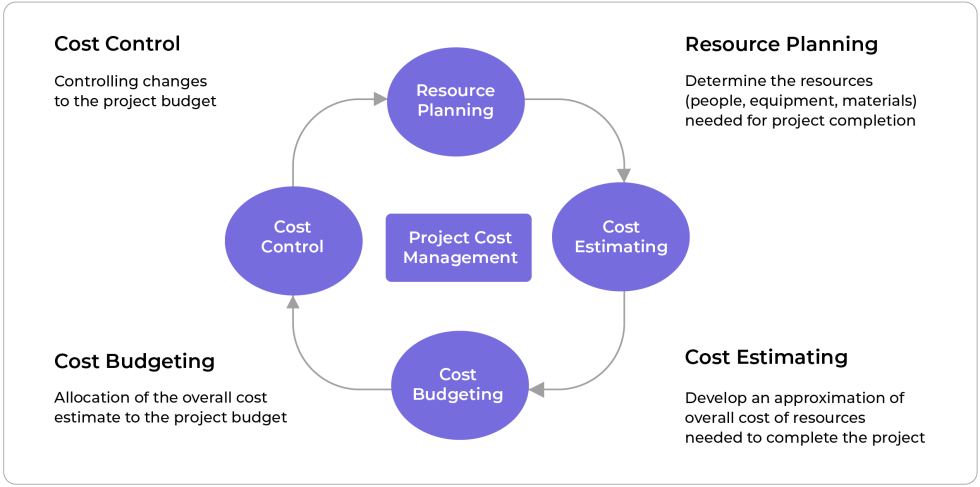
Project Resource Planning
Project resource planning is carried out in the planning stage of project development. It involves identifying the resources that are critical to execute and complete the project. These resources could be in the form of people, equipment, or technology.
However, to carry out project resource planning and determine the budget, project managers first need a work-breakdown structure. The task-level assignment of budget allows a granular project budgeting.
Cost Estimation
Estimating cost involves several activities, right from pricing all resources to preparing for risks. Given that project managers have to carry out in-depth research for cost calculation, it is considered one of the most intensive stages of a cost management plan. The project estimation must also account for disruptors like overheads, inflation, fixed or variable costs, and the time value of money.
Cost Budgeting
Some project managers may view project cost budgeting as a separate process, while others see it as a component of cost estimation. Either way, this segment involves the allocation of costs to the various tasks and sub-tasks of a project. It births a project cost baseline that allows project managers to measure and analyze the project cost performance continuously.
Cost Control
Cost control takes place throughout the project lifecycle. It deals with tracking the cost variances against the set baseline while also measuring project performance. Depending on the situation, project managers might have to take corrective action like reducing the scope or increasing the project budget to curb the variation disparity and align it with the projections.
Challenges Posed by Project Cost Management
Project cost management can be a hit or a miss. To improve your chances of nailing the cost management plan, here are some challenges that you may have to face and overcome:
- If the project budget is too restrictive, then your resource pool also shrinks up significantly. Resultantly, the project’s success comes under threat.
- The lack of skill or expertise in handling certain projects can result in cost overruns that could result in losing money.
- Outdated and obsolete project management software may cause project managers to lose accuracy and relevance while managing a project.
Project Cost Management Tips and Best Practices
The following are a few tips that can help manage costs effectively:
- While project managers determine the project budget, they must also account for inflation and its impact.
- Request for quotes from subject matter experts to gain realistic estimates.
- Factor in any potential events, such as natural disasters, that may weigh on your project budgeting or contribute to delays.
- Leave an adequate margin for unexpected costs through a contingency reserve so that you can meet random or unplanned expenses.
- Longer wait times between noticing cost discrepancies and taking corrective action mean that you would be losing more money. So act promptly.
- Framing a cost management plan is crucial for a project’s success, regardless of its size. So carry out project cost assessment and management even for small projects.
- Document everything as it may help with the cost management of future projects.
Final Thoughts
Project managers cannot gaze into a magic crystal ball to make accurate project budgeting predictions. However, thorough planning through a robust cost management plan can grant them the same capabilities. Leveraging project management software for cost management and control allows them to be more hands-on and vigilant. Real-time cost performance tracking and immediate deployment of corrective action is the formula for successful project cost management and foreshadows the success of the project!
