Project Management Guide
Project Management Guide
What Is Project Management?
What Is a Project?
Why Is Project Management Important?
Project Life Cycle Phases
- Project Initiation
- Project Planning
- Project Execution
- Project Monitoring
- Project Closure
Project Management Methodologies
- Waterfall Project Management
- Critical Path Method
- Critical Chain Project Management
- Agile Project Management
- Scrum Project Management
- Kanban Project Management
- Lean Project Management
- Six Sigma Project Management
- PRINCE2
- PRiSM
- PMBOK Method
Project Management FAQ
What is the critical path method in project management?
As project managers know, scheduling a project’s tasks correctly is a vital part of project management. It can make all the difference between a project that’s delivered on time and one that fails.
This is where the concept of the critical path method comes in. Simply put, a critical path is the sequence of tasks from beginning to end that has to be finished in order to complete a project. It gives you a bird’s eye view of the project and the estimated time needed. In the Project Management Body of Knowledge, a Critical Path Method is defined as: “the sequence of scheduled activities that determines the duration of the project.”
In this guide to this all-important process, we’re going to outline:
- How the Critical Path Method works
- The Critical Path algorithm
- Slack in the Critical Path Method
- Software and tools for determining the Critical Path
Be it the construction of a building, designing and launching a new product, creating software, or any other project, an understanding of the Critical Path Method is essential for success.
How does the Critical Path Method work?
As mentioned above, to find out a Critical Path, you have to first make a list of all the tasks required to complete the project. You also need to figure out the time that each task will take to complete.
There’s another step that’s vital. The dependencies between the tasks need to be mapped. This will help you to determine the order in which the tasks need to be carried out. After this, the Critical Path can be established by plotting the longest sequence of activities and estimating the total time for all of them.
It should be kept in mind that the time required to perform tasks that are not critical is not to be considered in total project time.
Let’s take a simple example. If the project is to waterproof the exteriors of a building, among the tasks will be to estimate and purchase the materials needed, employ workers, and measure the surfaces.
Then, you will need to ascertain other aspects that are dependent: whether an undercoat needs to dry before final application. Whether some surfaces need more attention than others. Whether certain areas need to dry completely before proceeding to others. And whether there are tests needed before moving on to completion.
Making a list of all this in order and then estimating the time will give you the critical path.
The Critical Path Algorithm
The example above was an extremely basic one, to outline the concept of the Critical Path Method. However, many projects are more complex than this.
In such cases, determining the Critical Path becomes not only more important but also more intricate. That is why many project managers rely on a Critical Path algorithm. This algorithm basically plots a task’s start time, duration, and finish time. It determines which ones need the most attention.
To do this, the algorithm needs to consider some factors. These are:
- Earliest start time (ES), which is the earliest time an activity can start.
- Earliest finish time (EF), which is simply ES plus activity duration.
- Latest finish time (LF), which is the latest time of finishing without delaying the project.
- Latest start time (LS), which is simply LF minus activity duration.
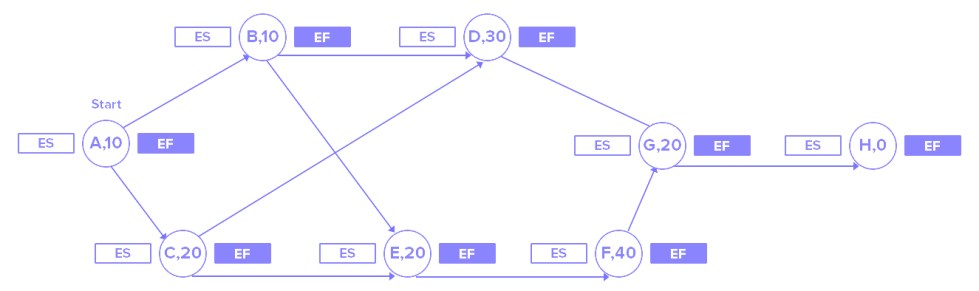
Apart from the above, dependencies need to be factored in, as these will affect the earliest start time of various tasks. Availability of resources to start and continue with tasks is another factor.
Not all projects require algorithms. It all depends on the complexity, number and nature of tasks, and the dependencies involved. Calendars, charts and other tools, which we will consider below, are also employed.
Slack in the Critical Path Method
Slack, which is also known as float, is an important aspect of projects. In the Critical Path Method, the amount of slack lets you know how long a task can be delayed until it has an effect on the overall project deadline.
If a task is included in the Critical Path, it should have zero float – it should be completed on time. If a task has a float of more than zero, it can be delayed without affecting the project completion time.
With this way of looking at projects, the difference between a job’s early start and its late start is known as total slack (TS). This is the flexibility built into the project. Such flexibility can be used to clarify and optimize work schedules. For example, if a machine has a period of time, it needs to rest and cool off, or if a team of people deserves more time off before starting on the next task.
Slack can also be divided in two ways: slack relating to the time the next task can begin, and slack relating to the overall project completion.
If the Critical Path Method is carefully applied with a proper estimation of dependencies and dates, slack becomes a valuable resource for the project manager to handle contingencies.
Software and Tools for Determining the Critical Path
We’ve already touched upon how algorithms can be used to determine the Critical Path. Fortunately for today’s project manager, there are a variety of project management tools to help determine the Critical Path with accuracy.
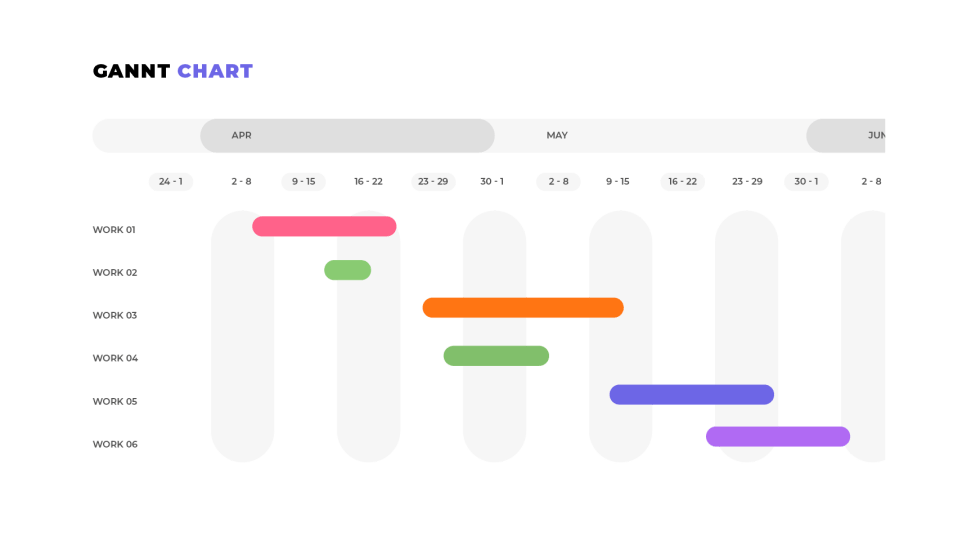
For example, with project scheduling software, the project manager can create project plans, view all upcoming tasks, and synch the deadline with automated calendars. With many projects, a Gantt Chart can be employed to get a visual overview of project tasks, dependencies, resources, and remaining tasks.
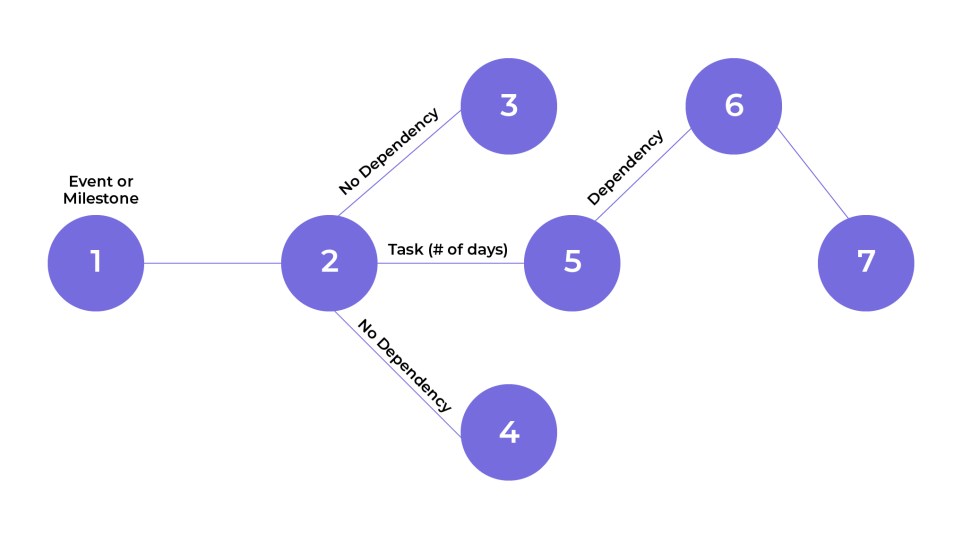
There are also PERT Charts, which can display the sequence of tasks on a critical path and the time to complete each. Factors such as the project float can also be viewed along with the start and finish dates of tasks.
With PERT Charts, information is presented as a flow chart. A Gantt Chart uses bars as a representation of a timeline.
What tools are best? That would depend on factors such as the nature and complexity of the project and the team’s familiarity with the processes used.
Plotting a Critical Path for a project is an essential step to make sure that there is not only a helpful overview but that the project can be delivered by the agreed deadline. It makes sense to spend time and effort at the start of any project to carefully plan the Critical Path.
