Chapter No. 1
The Basics of Project Management
Loreum Epsum

Every day that you get things done that you accomplish a coordinated series of tasks with the help of different pieces of information, tools, and people while controlling various events, you manage and successfully conclude projects.
Professionally, whether you work as a writer, a marketer, a software developer, a construction worker, a mailman, or an artist, and whether or not you are officially called a project manager, you have always managed a project.
It is said that project management is one of the oldest professions and that the oldest project is that of the Pyramids in Egypt, back in 2500 BC. If you look at modern instances of successful and memorable projects in the history of the world, the best examples could be the Hoover Dam, the Transcontinental Railroad project, The Manhattan Project, and many more around the world. The need for a more conspicuous framework for construction and manufacturing during the industrial revolution throughout the 19th-century lead to the birth of project management as we recognize it today.
Today, project management is more critical than ever, and 93% of organizations report using standardized project management practices (PMI).
Table of content
- What is project management?
- Why is it important to manage projects?
- What are the 5 phases of project management?
- How to streamline project management effectively?
- What are the types of project organizational structure
- What are the roles and responsibilities of a project manager
- How does Xebrio Help you Manage your Projects
What is project management?
Everything you do with a specific motive towards realizing an end goal, from estimating what a set of tasks needs to be like, what is required to be able to fulfill them, how exactly you will do them and when is called project management.
Project management is conceptualizing a plan to mold the resources available within a specific time, to accomplish a fixed, set goal.
Project Management Institute (PMI) defines Project Management as “the application of knowledge, skills, tools, and techniques to a broad range of activities to meet the requirements of a particular project.”
Similarly, the PMBOK® says project management is “The application of knowledge, skills, tools, and techniques to meet the project requirements.” The benefits derived from practicing proper project management are very valuable.
Project management is professionally carried out by a project manager who leads a team of professionals of varying types of expertise working on various aspects and requirements of the project in an organization. The project manager efficiently guides the project team through all phases of the project and aims to execute the project successfully.
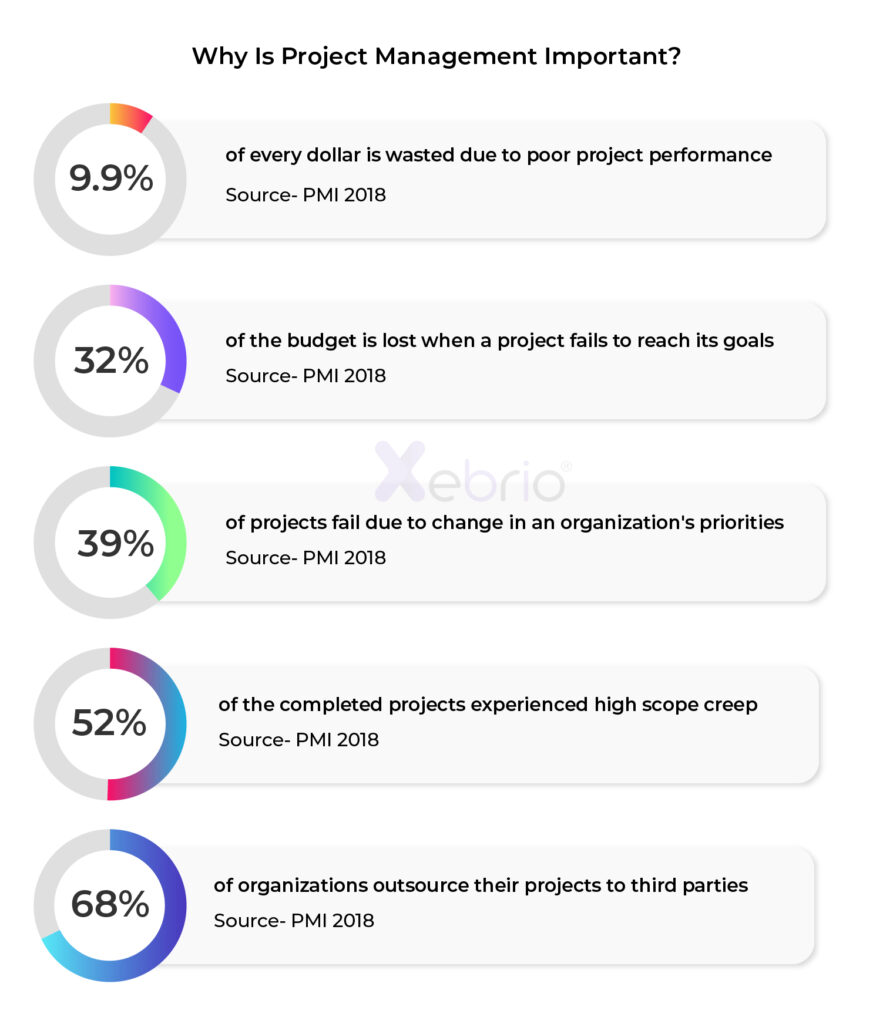
Why is project management important?
A Project Management Institute (PMI) survey states that only 58% of organizations actually understand the importance of project management. Project management has a host of benefits apart from boosting productivity, maintaining project transparency, and giving a clear path. Some of the benefits of project management are:A Project Management Institute (PMI) survey states that only 58% of organizations actually understand the importance of project management. Project management has a host of benefits apart from boosting productivity, maintaining project transparency, and giving a clear path. Some of the benefits of project management are:
- Better communication
- Improved resource management skills
- Increased customer satisfaction
- Tolerance of risk
- Better team spirit
- Increased output quality
Project management has been in existence as long as humans have been walking the earth. One of the earliest instances of projects are the pyramids of Giza. Right from the invention of the wheel to the invention of the device you read this on, everything has been a project. Someone had to oversee it, plan it, and work for it.
Project constraints such as scope wasn’t really a thing then but project timelines must have been. The project management practice was refined over the years and the methodologies evolved, starting with Fredric Taylor’s The Principles of Scientific Management in 1911.
Henry Gantt introduced the Gantt charts, Kanban and Lean came into existence with Toyota’s Taichii Ohno implementation in the manufacturing units back then. The Project Management Institute, PMI, was formed in 1969.
The project management methodologies were refined over the years with the introduction of newer concepts like Agile.
What are the five phases of Project Management?
Phases of project management comprise the necessary tasks, activities, and skills when completing a project. There are five major phases of project management listed below:
- Project Initiation
In the project initiation phase, one can determine high-level expectations about a project, the reasons for the project, its feasibility, and the requirements to complete the project.
This phase consists of stakeholder approvals, documentation related to the business case, approximate project resources required for project completion, and the stakeholders.
- Project Planning
The project managers list the scope, time, and risks in the planning phase. The main elements of a successful project plan are completeness and continuity.
This phase comprises a detailed project plan, a communication plan, a basic budget, project schedule, project goals, scope document, and an updated stakeholder registry.
- Project Execution
The project team members are taken through the communication plan to complete the work according to the project management plan.
The project execution phase allocates and manages the materials and budgets required for the project. In this phase, the project deliverables become the output.
- Project Monitoring and Controlling
The project monitoring and controlling phase compares the time, cost, and performance of the project at each point, and if required, make necessary adjustments to the project activities, resources, and plan in order to maintain the right track.
This phase includes project progress report and other communication materials that confirm sticking to the original project plan and avoid milestones and deadline disruptions.
- Project Closing
The project closure phase consists of project finalization, review of project deliverables, and conversion into a business leader.
In this phase, the project team can reflect on and celebrate the project. Project teams can apply their learnings to similar projects in the future.In this phase, the project team can reflect on and celebrate the project. Project teams can apply their learnings to similar projects in the future.
Why do projects fail?
At the start of a project, it might be impossible to imagine a highly-feasible project failing. Here are five primary reasons why projects fail:
- Resource allocation– incorrect resource allocation to complete a project.
- Insufficient time- inability to complete the project within the deadline.
- Uncertain goals- unclear details in a project document result in undesired results.
- Scope creep- project scope can change in the middle of the project that stakeholders do not agree upon at the start of a project.
- Lack of Risk management- not establishing the risks associated with every project can cause your project to fail.
How to streamline project management effectively?
All projects contain details, and to finish a project on time, it may be possible that you miss out on a couple of important ones. When project handling isn’t automated, it can get challenging to maintain all project details. This can drown project managers in unnecessary paperwork, increasing the chances of project failure.
It may seem impossible to wade through the chaos of a project, but there are several ways to streamline project management strategically:
- Freeze on stakeholder requirements and set a clear scope.
- Assemble the best project team.
- Design a realistic project schedule for maximum success.
- Outline project responsibilities within the team.
- Maintain an up-to-date project plan.
- Assign tasks according to priorities
- Finish the project with adequate resources.
- Keep stakeholder communication flowing.
- Set regular milestones to measure project deliverables.
- Anticipate changes and keep a flexible strategy in place.
- Proactively assess and manage project management risks.
- Invest in a robust project management tool.
The twelve steps listed above can help even non-project managers to successfully streamline their projects and complete within deadlines and budget.
Types of project management structures
Disproportionate project teams are one of the leading causes of project failure. The teams don’t have appropriate guidance of a proper organizational structure influencing the authority of project manager.
A project management structure defines the roles and authority within a project team and the organization with a hierarchical structure illustrating who reports to whom.
Based on the project goals and the nature of work, teams are structured the following way:
- Functional organizational structure
A functional organizational structure follows a hierarchical structure where vital decisions such as budget allocation, project schedule, and resource distribution lie with the upper management, which gives project managers almost no authority.
The work is divided into departments like sales, HR, and admin with pre-determined roles and responsibilities. As teams gain more experience, they get more skilled at what they do.
There are several disadvantages to this work structure:
- Repetitive work
- Poor collaboration
- Increased bureaucracy
- Projectized organizational structure
In this structure, the project manager is completely in charge and has authority over the budget, staffing, and scheduling. The project team members are included from different departments in an organization. Once the project ends, the team members return to their corresponding departments.
Within this project structure, there is minimum bureaucracy as communication is easier and decisions are made faster. Team members gain experience throughout the different range of areas as they work on different types of projects.
- Matrix organizational structure
The matrix organizational structure is an amalgamation of the two structures- functional organizational structure and project structure. In the matrix organizational structure, the reporting relationships are set up in a matrix or a grid. Project team members report to both the project manager and the functional manager. Their responsibilities are also divided; the functional manager helps to improve one’s project management skills, whereas the project manager determines the direction of the work.
The matrix organizational structure enables resource sharing. It empowers team communication and teamwork. This structure can be difficult to form as it has some conflicting pulls on the team and the resources it has. It can give rise to unnecessary conflicts and misunderstandings as the team reports to two different managers.
How does Xebrio Help you Manage your Projects
For some, the information given here maybe overwhelming, but most of you must be familiar with project management basics. If you’re working in the project management space, start using Xebrio project management tool.
Using Xebrio will not only hone your project management skills but also help you maximize your project’s success and help you chart a career path. Subscribe to the free trial and check out the tool for yourself.
Roles and Responsibilities of Project Managers
Project Managers are required to shoulder different roles and responsibilities with the people involved with the project such as:
- Interpersonal
- Work with professionals with different backgrounds within the team
- Resolve team conflicts
- Build positive relationships
- Encourage team members
- Projectized organizational structure
- Maintain effective communication with stakeholders
- Keep the team updated
- Conduct team meetings regularly
- Provide performance assessment
- Decisional
- Take varied decisions at every project stage
- Stay clear and committed
- Manage scope, time, and resources
- Prevent scope creep
- Management roles
- Hire and supervise employees
- Handle and balance budgets
- Address any ambiguity
- Adhere to business priorities
